Remote working has impacted the world of cybersecurity in multiple ways. Remote workers are often not protected by enterprise-level security and so are more prone to cyberattack. The FBI reported a 300% increase in cybercrimes since the pandemic began, and remote work has increased the average cost of a data breach substantially.
Employees working from home are also distracted –
“47% of remote workers cited distraction as the reason for falling for a cyberattack.”
In other words, if you do not have a plan in place to mitigate these risks, you are setting yourself up for a potentially devastating cybersecurity breach.
One simple way to protect your organization from breaches is to apply a strong password policy at all levels of the organization, and enforce it by implementing a secure password policy management solution (PPM).
Here are some password policy best practices you may find useful.
1. Increase password length and strength
Brute force attacks try all possible combinations of characters to arrive at the password. A 6 string password with only upper or lower case letters can be cracked in 8 seconds. An 18 character password with upper and lower case letters, numbers and symbols can take 1 quintillion years to crack! By adding a special character, combining both upper and lower case letters or adding numbers, encryption can be much more secure.
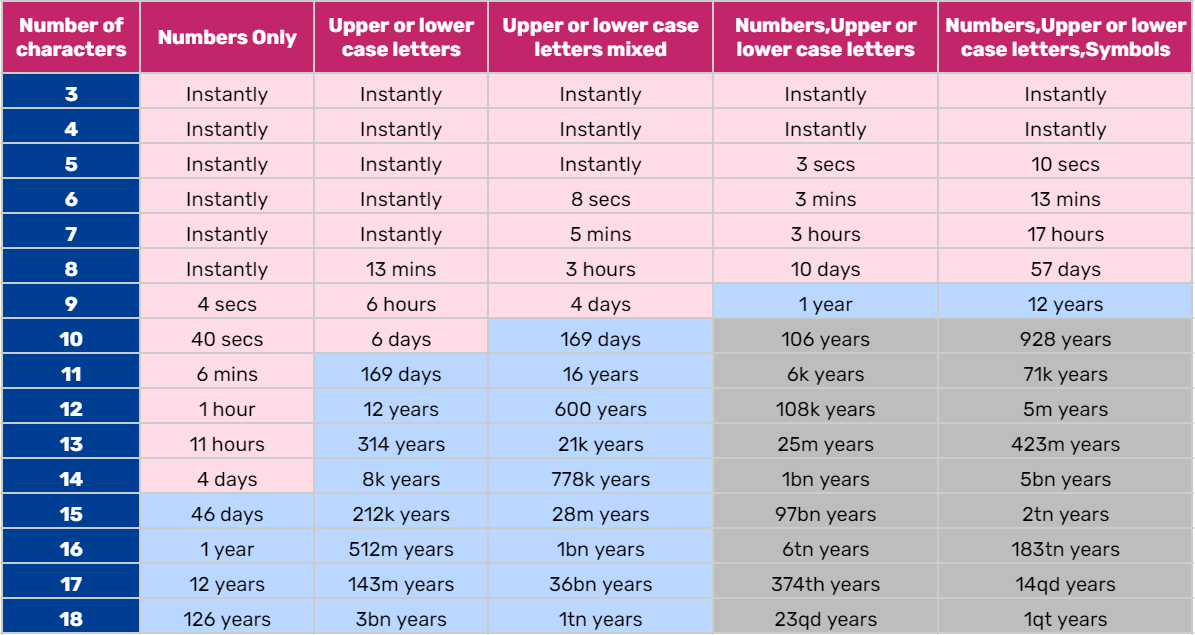
Image Credit: ghacks.net
The full strength of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) comes to bear when users create passwords of 32 characters for 128-bit encryption and 64 characters for 256-bit encryption. However, passwords of around 10 characters are strong enough for most applications.
2. Simplify as much as possible
A password made of only numbers has 10 options for each character in the string, one made of numbers and letters has 36 options, and if you include special characters that adds another 32 possible characters for each spot in the string. This makes it more challenging for brute force attacks to be successful. Complexity in terms of the kind of characters that can be used in the password is, therefore, an advantage.
However, do not mandate the usage of these different kinds of characters. This can lead to frustration and reuse of the same password with minor character substitutions (P@ssword or Passw0rd, for example). This is especially the case when the policy also demands frequent changes of password. If the old password is compromised, such minor variations will be relatively easy to guess, too.
To mitigate this risk, don’t mandate the use of special characters and reduce the frequency of mandatory password reset to approximately once a year. A long password using only lowercase letters is more secure than a short one which is a variant of an older password.
3. Do not allow password reuse
Do not allow reuse of earlier passwords during periodic password reset to increase security. Train your staff not to use minor variations of their earlier passwords, and instead look for completely different passwords.
Also train staff on the risks of reusing passwords across home and work accounts. Password reuse results in a huge surge in credential stuffing attacks. If any service is compromised and your password and username are stolen, hackers could use the same credentials to try and hack your other accounts. Each account must therefore use unique credentials to maintain security.
4. Reinforce passwords using multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication uses a combination of things you know, such as a password or PIN; things you have, such as a badge or smartphone; and things you are, such as biometric data, to authenticate your right to access a particular system, data or application.
Enabling MFA ensures that even if a password is stolen, the system is not compromised.
5. Use a secure password manager
Many users find it difficult to remember their passwords for multiple online services, and so either use a single password for all, or, worse, save all their passwords to an unreliable password manager.
If you do opt for a password manager, choose one that is highly secure, in order to mitigate the risk involved. Most IAM solutions will include a password manager or, with Single Sign-on, completely do away with the need for multiple passwords. A single secure password is enough to log on to your IAM and access your applications and data.
6. Use an IAM application for Password Policy Management (PPM)
It’s one thing to lay down rules for password policy across the organization. It’s quite another to enforce the policy. An Identity Access Management (IAM) application can help you ensure that all your users consistently comply with a high standard of security while setting their passwords, without the need for a separate password policy enforcement tool.
Administrators can customize and define password policy for all users in the organization. You can also specify upon whom the policy should be enforced, based on the users’ access level. Password policies can of course also be defined as blanket rules.
A common perception is that the risks associated with breached passwords do not apply to your organization as you have secure systems. But your organization’s data security is only as strong as the weakest password of your users. In 2020, 770 million credential stuffing attacks occurred. That means that if your employee’s personal passwords are compromised, and they have reused the same password at work, your data is compromised too. Worse, 17% of all sensitive files are accessible to all employees, and about 60% of companies have over 500 accounts with non-expiring passwords.
Implementing a robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) solution brings you several steps closer to protecting your user credentials and corporate data. Worldwide, cybercrime costs will hit $6 trillion annually this year. Don’t let your organization succumb to a Data breach! With these simple steps, you can stay safe with multiple layers of data protection. Allow our team at Akku to help you secure your systems.