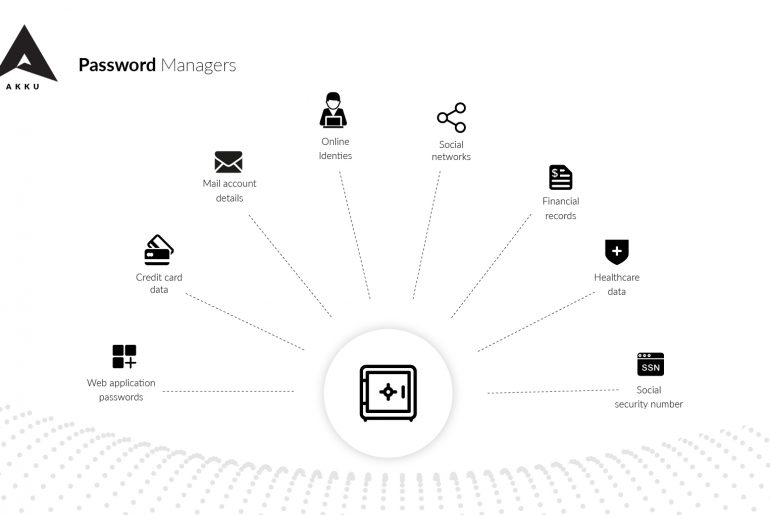
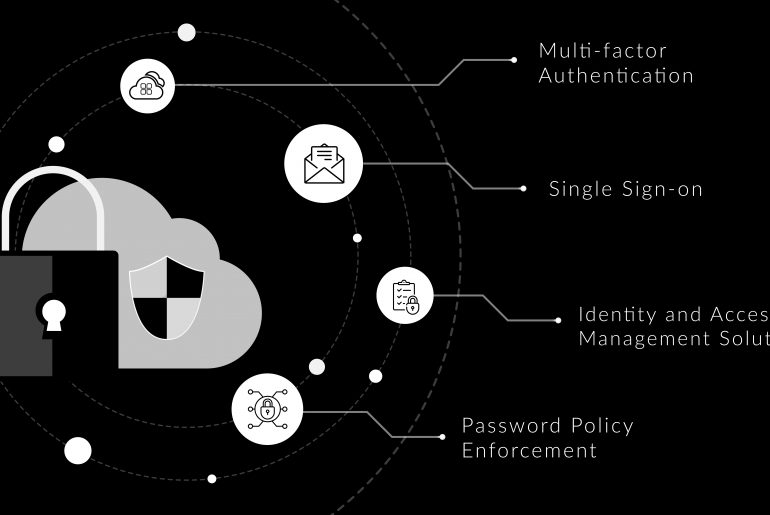
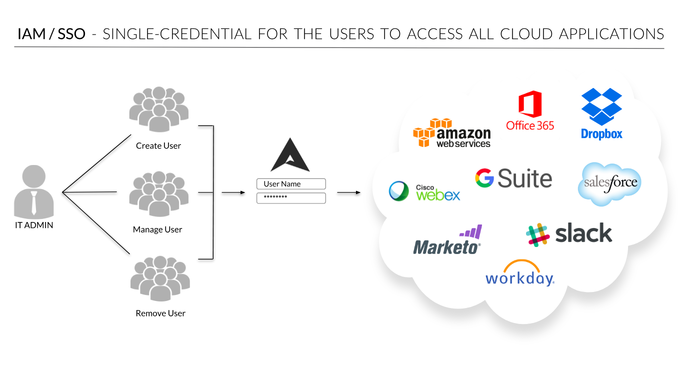
When large organizations like LinkedIn, Twitter and Facebook report password hacks, it throws some light on how vulnerable current systems are, as well as the need for multi-factor authentication. However, multi-factor authentication is shrouded in myths that may prevent organizations from adopting it.
Here, we have addressed a few of the most common myths surrounding multi-factor authentication.