If a company works with very few applications, user repositories would have to be mapped individually for each application. Every new user needs to be validated with each individual user directories to be able to access the respective protected application. This means that the same user has to log in separately every time he/she wants to use each application on the network. The inefficiency of this model was reduced greatly with the advent of Active Directory and LDAP.
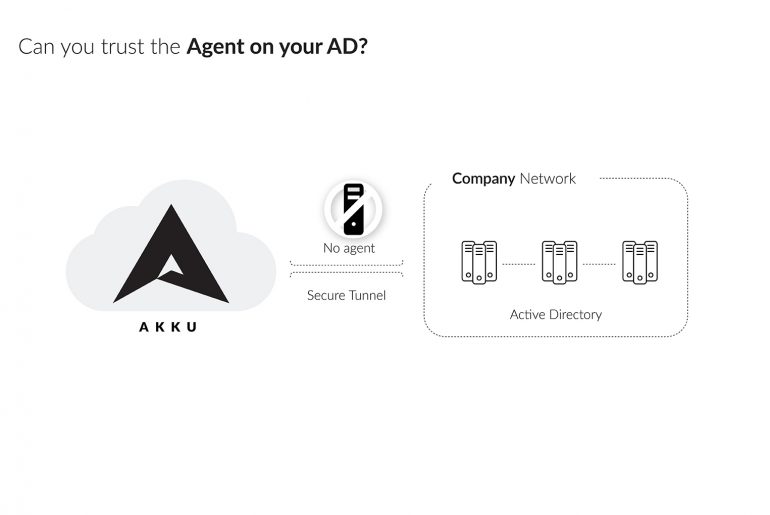
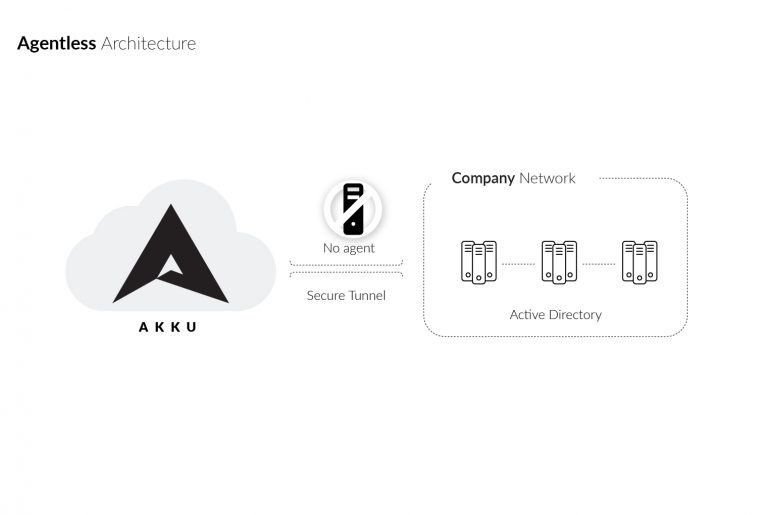
A significant number of identity and access management solutions have the need to work with Active Directory as the repository of user information against which access is verified. Active Directory generally controls user identity and access permissions to everything from files, networks, and servers, to on-premise and cloud applications. However, integrating an Active Directory or LDAP with on-premise and cloud applications require third-party agents to be installed on your network.